Learn how psychology can unlock engagement in B2B online communities by focusing on relationship-building and professional value, distinct from the emotion-driven strategies of B2C marketing. This article breaks down three psychological principles with actionable tips to create meaningful connections and sustained participation.
Article overview:
- Unique challenges of B2B online community engagement
- Three psychological principles: Scarcity, Elaboration Likelihood Model, and Psychological Ownership
- Practical applications and real-world examples for B2B contexts
Keeping members of a B2B online community actively engaged is no small feat, but it’s essential for customer loyalty and long-term business success. Unlike B2C communities — where engagement often hinges on emotional appeals, brand loyalty, or social trends — B2B communities thrive on relationship-building, knowledge-sharing, and fostering professional value.
The key to success lies in understanding what motivates this different audience to participate and contribute meaningfully. Psychology can provide powerful insights into their motivations, offering practical tools to address the unique challenges of engagement within the B2B context.
By applying proven principles, community managers can create spaces that attract members and keep them involved over time. This article will explore three such principles—Scarcity, Elaboration Likelihood, and Psychological Ownership—that can help you build a vibrant B2B community.
Principle 1: The Scarcity Principle
The Scarcity Principle is the idea that people are more motivated to act when they feel resources or opportunities are limited. When access is restricted, it taps into a psychological fear of missing out (FOMO) and drives demand.
Scarcity can be created through limited availability (like exclusive memberships) or limited-time offers, making users more inclined to act quickly or invest more deeply.
In B2C, scarcity often revolves around promotions like flash sales, exclusive product drops, or limited-edition items designed to create instant appeal. However, in B2B, scarcity is less about urgency and more about professional exclusivity or unique value.
Real-World Example: Moz’s Pro Q&A Forum
Moz, an SEO software provider, uses scarcity effectively with its Q&A forum, which is available exclusively to Pro members. This space allows subscribers to pose questions, receive expert answers, and interact with a community of SEO professionals.
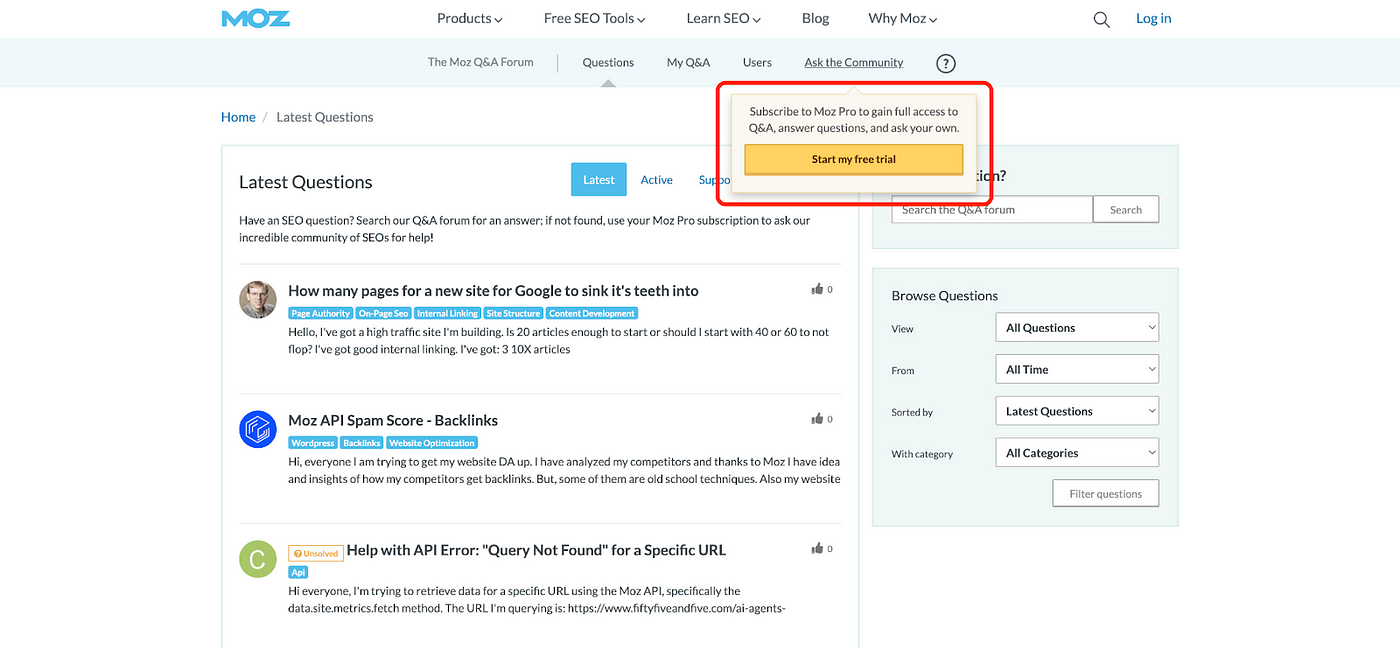
By making these valuable interactions open only to paid members, Moz enhances the appeal of its Pro subscription, driving user engagement and creating a tight-knit community focused on shared professional growth.
Unlike B2C communities that emphasise mass appeal, Moz’s approach demonstrates how B2B communities leverage scarcity to promote specialised knowledge-sharing and collaboration among professionals.
Practical Ways to Apply It
- Limited Real-Time Access: Host webinars or live Q&A sessions for a limited period. Announce them as “one-time events” to encourage members to attend and engage.
- Exclusive Content: Release special reports, templates, or insights that highlight unique professional value, exclusively to community members.
- Invite-Only Access: Create invite-only groups or discussions on relevant topics to give members a sense of being part of an exclusive circle.
Promoting scarcity in your B2B community creates a sense of exclusivity, but the focus should always remain on enhancing professional credibility and providing value for long-term engagement.
Principle 2: Elaboration Likelihood Model
The Elaboration Likelihood Model describes two ways people are persuaded: the central and peripheral routes.
In the central route, people focus on the quality of the message, considering detailed arguments and information to make an informed decision. This pathway is best for those interested in the topic and willing to process in-depth content.
In contrast, the peripheral route relies on external cues like visuals, credibility markers, or user popularity, appealing to those who prefer a faster, more surface-level interaction.
For B2C audiences, peripheral route strategies like eye-catching visuals or celebrity endorsements often dominate. However, in B2B, central route strategies take precedence because members prioritize actionable insights and expert opinions. Peripheral tactics still play a role but credibility markers like certifications or professional recognition may appeal more to B2B audiences.
Real-World Example: HubSpot Community Forum
Interestingly, HubSpot’s forum uses both routes to engage users. The central route offers in-depth resources — like webinars, whitepapers, and articles — that support users who want a thorough understanding of CRM and marketing practices. This engages those actively seeking to build knowledge or solve specific challenges.
At the same time, HubSpot’s use of peripheral cues, such as contributor badges or professional endorsements, adds credibility without relying on the aesthetic-focused tactics common in B2C settings.
Practical Ways to Apply It
- In-Depth Content for Central Route: Create case studies, reports, and webinars for users who value comprehensive resources. This is essential for B2B audiences who need detailed, actionable insights to drive decision-making.
- Quick Visual Cues for Peripheral Route: Use infographics and short videos for users looking for faster insights.
- Highlight Expertise: Show contributors’ credentials to appeal to users seeking trusted voices without deep investigation.
This dual approach makes your community accessible for both dedicated members and casual participants, with central-route strategies reinforcing the professional trust critical in B2B environments.
Principle 3: Psychological Ownership Theory
Psychological Ownership Theory suggests that people feel more invested in something when they believe it belongs to them, often because they’ve somehow contributed to it.
In B2B communities, fostering a sense of ownership can increase member loyalty and active participation, as members see themselves as integral parts of the community.
While B2C communities often build ownership through personalisation or interactive brand campaigns, B2B communities achieve this by empowering members to contribute knowledge and shape discussions. This approach aligns with professionals’ desire to gain influence and recognition within their fields.
Real-World Example: Salesforce Trailblazer Community
Salesforce Trailblazer Community encourages psychological ownership by enabling members to share insights, answer questions, and shape discussions. This hands-on involvement fosters a sense of belonging and expertise, helping members feel like co-creators in the community.
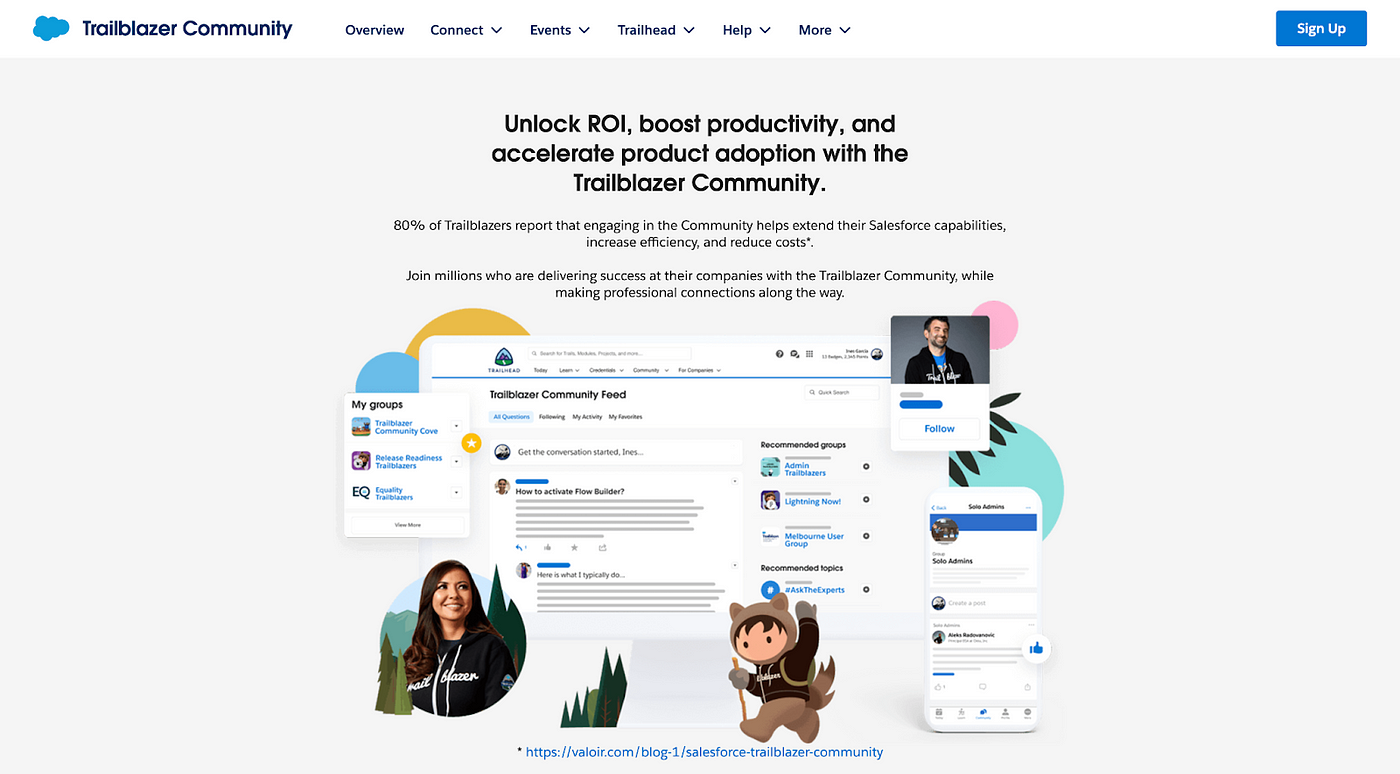
Compared to B2C, where ownership might be tied to personal experiences or consumer choices, Salesforce’s approach shows how B2B communities emphasise professional impact and collective growth.
Practical Ways to Apply It
- Encourage Content Creation: Allow members to create content, such as tutorials, best practices, or insights, which makes them feel responsible for the community’s growth.
- Reward Contribution: Implement badges or recognition for members who actively contribute, like solving queries or leading discussions.
- Give Voting Power: Let members vote on topics or issues to be discussed or addressed, reinforcing their sense of influence and importance within the community.
Promoting psychological ownership nurtures loyalty and turns passive members into active participants as they create an impact through their contributions, big or small, to a community they belong to.
Start small, start now
Engaging an online community requires strategies rooted in understanding user behaviour. For B2B communities, the goal is not just to capture attention, as in B2C, but to also cultivate lasting professional relationships that drive mutual growth.
By leveraging the Scarcity Principle, you can create exclusivity that drives action. The Elaboration Likelihood Model helps you cater to deeply invested and casually engaged users, while Psychological Ownership fosters a sense of belonging and long-term loyalty.
Experimenting with what works best for your community does not have to be overwhelming. Start small and start today because while applying these principles may take time and refinement, the payoff — a vibrant, thriving community — is worth it.

Leave a reply to How to Generate More Leads with Proven Outbound Marketing Approach – Vanesse Tang Cancel reply